What Are The H's and T's?Advanced cardiac life support (ACLs/ALS) classes prepare a healthcare provider for events relating to sudden cardiac arrest including basic life support (BLS) and airway management skills. However, once resuscitation events have proven successful it is also important to identify any reversible causes of the abnormal arrhythmia and cardiac arrest. This is the point where an in-depth understanding of the H's and T's is critical. Summarizing the H's and T'sThe H's and T's are a mnemonic device to help you remember the different contributing factors to sudden cardiac arrest due to pulseless electrical activity (PEA), asystole, ventricular tachycardia (Vtach), or ventricular fibrillation (Vfib). An increased understanding of these factors can help you find underlying causes due to any of these events. The H's1. Hypovolemia: Hypovolemia occurs when the body loses a large amount of blood or fluid due to severe blood loss, vomiting or diarrhea, dehydration, and excessive sweating. 2. Hypoxia: Hypoxia is a condition exhibited by decreased oxygen levels throughout the body or in a specific area. Hypoxia may be caused by various pre-existing medical conditions, drowning, trauma, or a brain or spinal cord injury. 3. Hydrogen Ion (Acidosis): Acidosis occurs when there is a buildup of hydrogen ions that impair the circulatory system and reduce oxygen into the lungs. Both metabolic and respiratory acidosis may lead to cardiac arrest. 4. Hyper-/Hypokalemia: These are metabolic disorders which involve abnormal potassium levels which can lead to cardiac arrest. Hyperkalemia occurs when potassium levels get too high, while hypokalemia is characterized by low potassium. 5. Hypothermia: Hypothermia occurs when a person’s body temperature drops below 86°F. Although it is not a common cause of cardiac arrest, it should be considered in some circumstances, especially drowning. The T's1. Tension Pneumothorax: This condition occurs when air becomes trapped in the pleural space. The buildup of tension can lead to cardiovascular collapse, which is life-threatening. It can occur due to respiratory diseases, trauma, or other factors 2. Tamponade: Cardiac tamponade occurs when fluid accumulates in the pericardium, which prohibits the heart from pumping blood normally. It is often caused by trauma or inflammation of the pericardium. 3. Toxins: This condition can be caused by an accidental overdose of any number of medications which can lead to cardiac arrest. Some of the most common include tricyclic antidepressants, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, benzodiazepines, opiates, and barbiturates. 4. Thrombosis (Pulmonary): Pulmonary thrombosis occurs when there is a blockage in the primary lung artery. It often occurs due to deep venous thrombosis (DVT). 5. Thrombosis (Coronary): Coronary thrombosis is in the majority of cases caused by disruption or fissuring of an atherosclerotic plaque. Application of Knowledge of H's and T'sUnderstanding the H's and T's of cardiac arrest and reversible causes is a vital part of any ACLS/ALS training. By knowing the aforementioned reversible causes allows the healthcare provider to respond quickly to the underlying problem and possibly prevent additional complications from occurring. The H and T mnemonic presented will allow you to quickly evaluate possible causes, while also ensuring you can respond to any additional patient needs and concerns. Would you like to take your knowledge and your patient care to the next level with ACLS/ALS certification with us here at Help-A-Heart CPR. With classes online, in-person, and on-site, you can find a course that fits your busy schedule. Contact us today to learn more about our class options or check out our current class schedule today.
Comments
Four Things About Waveform CapnographyWaveform capnography is one of the most important vital signs used to monitor a critically ill patient. The waveform capnography reading provides information regarding the tracking of ventilations, airway placement, and the measurement of carbon dioxide during exhalation. Through the use of capnography, a patient’s ventilation status is monitored in real time. Health care providers are able to identify potential breathing complications (such as airway obstruction, hyperventilation, hypoventilation, or apnea) and respond accordingly with a change in clinical management. What does waveform capnography tell us?Waveform capnography indicates how much CO₂ is present during each phase of the respiratory cycle, from inhalation to exhalation. It also displays respiratory rate. Capnography measures ventilation, rather than oxygenation. Ventilation encompasses the air movement both into and out of the lungs, while oxygenation lets you know how much oxygen is inhaled by the lungs and reaches the bloodstream. Monitoring VentilationCapnography waveforms reflect the amount of CO₂ in exhaled air, known as the end-tidal carbon dioxide or EtCO₂. End-tidal carbon dioxide (EtCO₂) is the level of carbon dioxide that is released at the end of an exhaled breath. EtCO₂ levels reflect the adequacy with which carbon dioxide (CO2) is carried in the blood back to the lungs and exhaled. Causes of Respiratory DistressDifferent capnography waveforms can indicate conditions like cardiac arrest, shock, asthma, pulmonary embolism, and emphysema. An assessment of the waveform capnography allows the healthcare provider to detect occurrences of bronchospasm, hyperventilation, or respiratory failure. By understanding the PQRST of the waveform, you can rapidly assess possible causes for the respiratory distress and provide the appropriate treatment. The PQRST includes the following: 1. Proper: means that you should know the normal readings for quantity, rate, shape and trending of EtCO2. In this case, normal means what we find in a healthy person with no metabolism, ventilation or perfusion problems. 2. Quantity: target EtCO2 value should be 35-45 mmHg. 3. Rate of ventilation: should be 12-20 breaths per minute (bpm) for adults if the patient is breathing on their own and 10-12 bpm if you’re ventilating them. Children should be ventilated at a rate of 15-30 bpm; 25-50 bpm for infants. Ventilating too quickly won’t let enough CO2 build up in the alveoli, resulting in lower EtCO2 readings. Ventilating too slowly will allow extra CO2 to build up, resulting in higher readings. 4. Shape: of the waveform should normally be a rectangle with rounded corners. Different waveform shapes can indicate different conditions. 5. Trending: of the quantity, rate and shape of EtCO2 should be stable or improving. Monitoring Treatment EfficacyThe waveform capnography reading can advise the healthcare provider on how effectively a specific treatment is working. If the treatment does not produce the desired effect or there are sudden changes to the waveform, this assessment of the reading can allow the healthcare provider to identify the issue quickly so a modification to treatment can be made a seamless and effective manner. Detection of ShockThe waveform capnography reading can also provide information about the circulation throughout the body. A decreasing EtCO₂ may indicate the early stages of hypotensive shock related to reduced cardiac output, which is the most effective time to begin treatment. Capnography can also provide feedback on the effectiveness of chest compressions during cardiac arrest. Understanding of Capnography Essential to Emergency Medical CareThe assessment of the waveform capnography reading provides important data which allow healthcare providers to effectively diagnose and treat patients in cardiac arrest, as well as respiratory distress and shock.
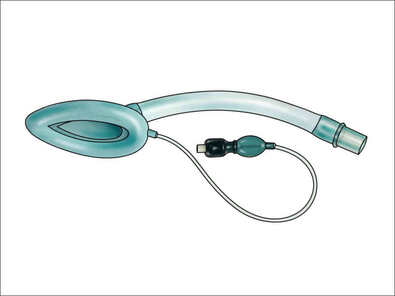
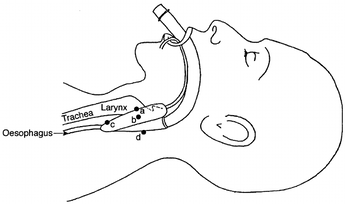
Would you like to learn more about certification training and our class schedule here at Help-A-Heart CPR? Or, would you like to learn more about waveform capnography and take your skills to the next level? We offer advanced training including ACLS/ALS certification and in-person ECG and pharmacology courses that will help you advance your career and optimize your personal skills and knowledge. What is a Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA) ?The LMA is a supraglottic airway device that was first designed for elective ventilation in the operating room. The use of the LMA is an often preferred alternative to bag-valve-mask ventilation allowing the healthcare provider to monitor the patient rather than holding the mask in place. The LMA is also minimally invasive and designed specifically for airway management in the unconscious patient. Subsequently, an inflatable mask is fitted with a tube that exits the mouth to permit ventilation of the lungs. History of the LMAThe laryngeal mask airway (LMA) is a supraglottic airway device developed by British Anesthesiologist Dr. Archi Brain. It has been in use since 1988. Types of Laryngeal Mask AirwaysThe LMA comes in an assortment of sizes and styles. The different types of laryngeal mask airways include: 1. LMA Classic: the original, reusable device 2. LMA Unique: a disposable version that works well in the field 3. LMA Fastrach: an intubating LMA that easily precedes intubation 4. LMA Flexible: softer tubing, not appropriate for emergency situations 5. LMA ProSeal: used to suction gastric contents, not appropriate for emergency 6. LMA Supreme: similar to the ProSeal, but includes a built-in bite block 7. LMA CTrach: includes built-in fiber optics with a video screen When Do You Use a LMA?The LMA is used as temporary airway during anesthesia or as a life-saving measure when respiration is not present. The LMA is often useful in the operating room, intensive care unit, emergency room, and by paramedics and EMT's. The Anatomy of the LMAThe LMA consists of an endotracheal tube that connects to an elliptical mask on the distal end. The mask features a cuff that forms an airtight seal on the glottis once it is in place. The mask of the LMA is inserted first, with the mask covering the glottis and the tube extending out of the patient’s mouth. LMA devices range in size from 0 for an infant to 6 for a large adult. The specific size is determined by the age and weight of the patient. When a patient is between mask sizes, the larger size is usually recommended to ensure a secure seal. How To Insert an LMATo insert an LMA, follow these steps: 1. Inflate and deflate the cuff to check its volume and ensure there are no leaks. 2. Apply the lubricant to the posterior surface of the mask. 3. Pre-oxygenate the patient with bag-valve-mask ventilation if possible. 4. Position the patient in the sniffing or "neutral" location. 5. Insert the LMA and manually guide it along the hard and soft palates and into the throat by pushing with the index or long finger in the v-shaped notch where the tube attaches to the mask. 6. Use minimal pressure to advance the LMA until you encounter resistance. 7. After the LMA is in place, then inflate the cuff. Help-A-Heart CPR has the classes you need to stay current and advance your career. Check out our class schedule today to find the right training for you.
What is Return of Spontaneous Circulation (ROSC)?The return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) is the primary goal of resuscitation of a cardiac arrest patient using basic and advanced life support measures. What happens during cardiac arrest?Cardiac arrest can occur when the heart’s electrical system stops working properly, which can lead to an abnormal heart rhythm. In addition, besides constant palpation of a carotid pulse, waveform capnography is the most reliable prehospital monitoring device to detect the immediate loss of circulation. Lastly, providing high quality CPR, sometimes combined with defibrillation, can be used to attempt resuscitation with the ultimate goal of achieving ROSC. What are a Few Signs of ROSC?A few signs of ROSC might include: 1. Movement 2. Coughing 3. Breathing 4. Detectable pulse 5. Measurable blood pressure 6. Increase in ETCO2 Although ROSC is a positive sign and the ultimate goal of CPR, post-resuscitation care must be tailored to the needs of the individual patient. A clinical Look at rosc in mEDICINEThe measurement for ROSC involves the assessment of noticeable signs like breathing or movement, as well a fluctuations in ETCO2. A sudden increase in ETCO2 is often the first sign of return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC), even before a carotid pulse can be detected .Some of these causes might become apparent during resuscitation of the patient, especially while evaluating the 5Hs and 5Ts of cardiac arrest. In order to achieve ROSC it is critical to focus on the advantages of high-quality CPR with adequate chest compressions and rescue breaths. The ability to achieve the proper compression depth, minimize compression interruptions, and the addition of antiarrhythmic drugs will often proven advantageous for the patient resulting in ROSC. CPR Training to achieve rosc!As a healthcare provider or caregiver, it is important to provide patients the best odds of ROSC by knowing and understanding high-quality resuscitative measures. A CPR and AED certification class gives you the chance to review your knowledge and practice your skills so you are prepared to provide lifesaving measures in a cardiac emergency. Help-A-Heart CPR offers training classes taught by experts in the field who are committed to making training informative and fun. With better focus during class and greater retention afterward, you will be equipped to give your patients the highest level of care possible.
Help-A-Heart CPR offers classes at our Texas locations, as well as online and on-site. Contact us today to get our current class schedule. What's The Difference Between American Red Cross BLS vs. American Heart Association BLS?If you have recently taken a Basic Life Support (BLS) class you probable noticed that there are several options including the American Red Cross (ARC) BLS and the American Heart Association (AHA) BLS class. In this post, we’ll explain the differences between the two curriculums so that you can choose the right one for you. How are the bls guidelines established?All BLS courses are based on the guidelines from International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR). ILCOR publishes the guidelines and then the American Heart Association, American Red Cross, American Safety Health Institute and all other training providers base their courses off of that material. Curriculum COMparison: AHA vs. arc1. Course Duration and Instruction Models: The American Heart Association and American Red Cross BLS course durations are different. The American Red Cross Basic Life Support course lasts approximately 4.5 hours and/or the American Red Cross BLS Blending learning in-person session lasts 2.5 hours. The AHA BLS is approximately 3.5 hours and/or the in-person BLS skills testing is 30 minutes. Student's have the option of either a 100% in-person class or the hybrid and blended learning model. Please keep in mind that the hybrid or blended learning class also includes an online course portion which can vary in time from 2.0 hours to 4.0 hours based upon proficiency and prior knowledge.
2. Course Methodology: The American Heart Association has two training options available. Students can choose between blended learning, online sessions with an in-person skills check, or traditional classroom training. The American Red Cross also offers both hybrid and traditional sessions. Are you confused about which class to take? For experienced healthcare providers we recommend hybrid online BLS training. For new providers, or those that are not providing CPR on a regular basis, we recommend the traditional, instructor-led class. That way you’ll get more practice time and be able to ask all of the questions you want. 3. Certification Acceptance and Recognition: Both the American Heart Association and the American Red Cross are widely accepted throughout various industries. We always recommend that you consult with your employer to see which curriculum is required. The American Red Cross is a well-known emergency response organization established in 1881. The American Heart Association is also a recognizable national organization. It was founded in 1924 and has since grown into the U.S.’s largest voluntary organization focused on heart disease and stroke. 4. Comparison of Cost: The cost of the BLS certification varies based on the curriculum model and whether class is a hybrid or blended learning version or a 100% face-to-face instructional model. The American Heart Association and the American Red Cross offer digital certification cards for your convenience. The American Red Cross and American Heart Association also have an online portal for students to access their e-cards and both share and print their certifications. Take a BLS training course with Help-A-Heart CPR and earn your AHA or ARC BLS certification today. If you have any additional questions regarding the BLS provider certification please feel free to email us or call us to learn more about our classes and course availability. How To Renew Your BLS Certification?How long has it been since you've taken a BLS certification class? The processing of renewing your American Heart Association BLS certification is integral to your profession as a healthcare provider. Renewing your BLS certification also gives you an opportunity to review your skills as a healthcare provider while also remaining current on your certifications and credentials. Are you Ready to take a BLS Provider Certification Class?At Help-A-Heart CPR, we strive to make the initial certification and the recertification process easy from start to finish. Our registration process is simple and convenient. We offer training at several different locations and at a variety of days and times to help accommodate everyone's busy lifestyle. To begin, simply visit our main registration page and then search for BLS Provider, BLS Renewal, or Heartcode BLS Skills Testing classes based upon your preference. Then click through to view the class schedule. How Do I renew a BLS certification?The BLS certification classes at Help-A-Heart CPR are an efficient and convenient way to renew your AHA BLS credentials. Our blended learning classes allow you to complete part of the training online, whenever and wherever is best for you. This is a great option for those looking to renew because you can complete the course at your own pace. This method of learning offers the same high-quality materials and lessons as a traditional classroom, with all the benefits of a virtual class. To enroll, just register for a Heartcode BLS Skills Testing certification class time slot and location that fits your schedule. You will then need to purchase the American Heart Association Heartcode BLS online course to get access to the self-paced online training modules that can be completed at your convenience. After completing the virtual modules, visit one of our offices to complete the brief skills practice and test. Once you’ve passed the exam, you’ll receive a American Heart Association BLS card within 48 to 72 hours to prove your certification. You can show this to your employer to let them know that you have renewed your certification. It remains valid for 2 years after the date you complete the training course. Once your certification has expired, just head back to Help-A-Heart CPR for another renewal course! Who Should Complete The American Heart Association BLS Certification Class?Taking a BLS Provider certification class can offer many benefits for individuals not to mention that it is most often a requirement to work in a clinical setting with patients. The following are just some of the roles for which BLS training is recommended: 1. Doctors 2. Registered nurses 3. EMTs 4. Dentists 5. Pharmacists 6. Medical personnel If you’ve taken a BLS class in the past, you will need to renew your American Heart Association BLS card every 2 years What Topics Will Be Discussed in a BLS Certification class?During a BLS certification course, we will cover a wide number of subjects related to Basic Life Support (BLS) including the following: 1. How to provide CPR for adults, children, and infants 2. Care for conscious and unconscious choking victims of all ages 3. Use of the Automated External Defibrillator (AED) and special considerations 4. How to use breathing barriers and bag valve masks 5. What to do in a 2 rescuer CPR situation 6. Treatment for cardiopulmonary emergencies and special situations Renew Your BLS Certification AT Help-A-Heart CPR!Are you ready to renew your American Heart Association BLS certification? There’s no better option than a course from Help-A-Heart CPR. We understand that everyone has a busy schedule nowadays and our goal is to provide a learning environment that is both relaxed and yet empowering. That’s why we go above and beyond to support our students with nearby destinations, frequent class times, and helpful instructors. Our BLS certification courses combine high-quality lessons and engaging interactive practices so that each student leaves the classroom equipped with the skills and knowledge they need to be successful. With years of in-field experience, our team of experts is ready to answer your questions, provide valuable advice, and share memorable anecdotes along the way. Contact Us!If you’d like to learn more about the American Heart Association BLS certification and renewal classes, don’t hesitate to reach out. Use our online contact form or give us a call at (210) 380-5344. You can also learn more by visiting our registration page.
What Are Bloodborne Pathogens?Potential contact with another person’s blood or bodily fluids should warrant extreme precautions. These precautions are needed due to the inherent risk posed by bloodborne pathogens in which microorganisms capable of transmitting bloodborne diseases such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and Hepatitis B (HBV). So what exactly are bloodborne pathogens? Bloodborne pathogens are microorganisms in human blood and other bodily fluids that can spread infectious bloodborne diseases. These diseases are spread through contact with infected materials such as contaminated needles, through an open wound, mucous membranes, or damaged tissues. Three Common Bloodborne DiseasesOf the 20 bloodborne pathogens known to cause diseases such as malaria, syphilis, and hemorrhagic fever, there are three; hepatitis B (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) that are the most common pathogens of concern. These three viruses account for the majority of occupationally-acquired infections and are associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Hepatitis C: Hepatitis C (HCV) is an infection that affects the liver, spread by contact with an infected individual’s blood. HCV can be a short-term illness for some, but for others, it can result in a long-term illness or even lead to life-threatening conditions including cirrhosis or liver cancer. If it is detected early, HCV is treatable. However, symptoms often do not become apparent until the infection has progressed into advanced liver disease. There is no vaccine for HCV, so the best way to avoid contracting it is by avoiding contact with infected blood. Hepatitis B: Hepatitis B (HBV) also impacts the liver, however unlike HCV, there is a vaccine for Hepatitis B. HBV is spread through the blood, semen, or bodily fluids of an infected individual. The virus does not always present symptoms and it can be a short-term illness when detected early. For others, the virus can turn into a chronic infection or cause other serious conditions like cirrhosis or liver cancer. HBV can be detected from symptoms like stomach pain, fatigue, and jaundice. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV): Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), is also one of the most common bloodborne pathogens. The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) targets the immune system causing acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). HIV is transmitted via direct contact with blood, semen, rectal fluids, vaginal fluids, or breast milk from an individual with a detectable viral load. In the workplace, occupational transmission is influenced by several factors, including volume of blood, type of procedure, type of injury, or percutaneous penetration. Compared to HBV and HCV, the percutaneous risk of HIV transmission is the smallest, estimated to be around 0.3%. There is currently no cure for HIV, but it can be treated and controlled with medical care How to protect yourself from bloodborne diseases?According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration various factors that can help reduce the transmission of bloodborne disease include the following: 1. Blood and body fluid precautions for all patients, regardless of infection status. 2. Hand hygiene. 3. Separating food and drink from areas where blood and bodily fluids are present. 4. Use of gloves, gowns, masks, eye protection (e.g., goggles), face shields when in a healthcare environment. 5. Safe waste management. 6. Safe laundry management. 7. Post exposure evaluation and follow-up after occupational exposure to a bloodborne pathogens. Whether a healthcare provider or not, it is important to use precautions when exposed to blood or bodily fluids. At Help-A-Heart CPR we provide training on bloodborne diseases and precautionary measures in our Bloodborne Pathogens training as well as our American Heart Association First Aid and American Red Cross First Aid classes. Take a moment to review our training schedule or call us to register for an upcoming class.
Do You Know The Symptoms and Treatment for Food Poisoning?Food poisoning can occur when you eat or drink something that is contaminated with harmful bacteria which have multiplied, either from poor handling, improper cooking, or poor food storage. There are specific foods that are most likely to cause foodborne illness, such as undercooked seafood products, undercooked deli meats and ground beef, unpasteurized milk, cheese, and juice raw, and unwashed fruits and vegetables. In addition, other factors such as parasites, toxins, chemicals, and viruses, can also contaminate food during the production and processing phase. Who's at Risk For Food Poisoning?Food poisoning can negatively impact most individuals. However, certain demographics are more prone to foodborne illnesses than others, such as: 1. People with weakened immune systems 2. Diabetics 3. People with Acquired Immunity Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) 4. People undergoing chemotherapy for cancer 5. Pregnant women What Are The Common Symptoms of food poisoning?The symptoms of food poisoning can vary depending on the source of the infection. Most types of food poisoning cause one or more of the following symptoms: 1. Vomiting 2. Watery diarrhea 3. Loss of appetite 4. Nausea 5. Stomach cramps 6. Headache 7. Mild fever 8. Weakness Food poisoning symptoms that are potentially life-threatening include: 1. Diarrhea that lasts for more than three days 2. A fever greater than 102°F 3. Difficulty seeing or speaking 4. Symptoms of severe dehydration 5. Bloody urine You must immediately contact a doctor or seek medical treatment if you notice or experience these severe symptoms. Food poisoning First AidIn the event you suspect someone has food poisoning, please follow the guidelines below: A. Advise them to lie down. If they vomit, give them small sips of water to drink, which will help prevent dehydration. B. If they have accompanying diarrhea, replacing lost fluids and salts is vital. You can advise them to take an ORS (Oral Rehydration Solution) as directed on the packet from your local pharmacy. C. When they feel hungry, advise them to eat light, bland food easily digested, such as bread, rice, crackers, or a banana. D. Do not drink caffeine, alcohol, or fizzy drinks. E. If the symptoms worsen and the vomiting and diarrhea persist, seek medical advice. F. Do not take anti-diarrhea medicines unless specifically advised by a healthcare professional. G. Children with food poisoning should avoid dairy products and drink plenty of fluids. When To Call EMS?There are two ways to get help from food poisoning in the United States – the Emergency Medical Services team or the Poison Control Center. They are excellent resources for poisoning information and, in many situations, may advise that in-home observation is all that’s needed. You should Call 911 immediately if the victim of food poisoning is: 1. Drowsy, unconscious, or not breathing 2. Having seizures 3. Having difficulty breathing 4. Uncontrollably restless or agitated 5. Known to have taken medications or any other substance overdosed. If the person is stable and has no symptoms or if the person is going to be transported to the local emergency department, you should call the Poison Control Center. When speaking with the poison control center, be ready to describe the person’s symptoms, age, weight, other medications they are taking, and other information you have about the poison. It would be best to know the amount ingested and how long since the person was exposed to it. If possible, have the pill bottle, medication package, or other suspect containers on hand to refer to its label. Enroll in a CPR/AED/First Aid Class!At Help-A-Heart CPR we offer the CPR and Basic First Aid Class which will teach you everything you need to know about poisoning symptoms and treatment. Give us a call today or take a moment to review our class schedule to find a First Aid class that meets your training needs.
Can You Perform CPR on a Pregnant Woman?The first question is "Can you perform CPR on a pregnant woman"? Yes. If a pregnant woman is experiencing cardiac arrest, you absolutely should perform CPR. According to the American Heart Association (AHA), “Resuscitation of the pregnant woman, including PMCD when indicated, is the first priority because it may lead to increased survival of both the woman and the fetus.” While it makes complete sense that that bystanders may be hesitant to perform CPR when the patient is noticeable pregnant simply of of fear of harming the mother or the baby. However, it is important to know that CPR is still recommended for pregnant patients and immediate action is necessary. When a patient receives immediate CPR, their odds of survival increase by over 40% Subsequently, it is vital that CPR is administered to a pregnant women when signs of cardiac arrest first become noticeable. How do you perform CPR ON A PREGNANT WOMAN?1. Call 911 or EMS. Upon recognition that the pregnant woman or victim is unresponsive and not breathing, immediately call 911. Next, while you are speaking to the 911 dispatcher please ensure that you let them know that the patient is pregnant so that first responders are prepared and aware of the essentials for this medical emergency. 2. Perform CPR Next, while waiting for the emergency personnel to arrive on the scene, you should begin administering CPR to the individual. Make sure that the pregnant woman is lying on her back in the supine position on a flat, hard surface like the ground or the floor. You’ll need to open the airway and confirm that the patient is not breathing properly. Then, begin delivering chest compressions. A special position for administering compressions is not needed for the pregnant woman so you can press down on the center of their chest as is standard for any patient who requires CPR. Lastly, perform hard, fast compressions at around 100-120 beats per minute and at a depth of around 2 inches or slightly more. 3. Use an AED When the AED arrives at the scene, it is important to immediately use it. First, turn on the device and follow the audible prompts provided by the AED. The device will either instruct you to deliver the defibrillation shock or to continue with CPR if it assesses that a shock is not necessary. The implementation of AED shocks are considered safe for women at any stage of pregnancy and harm to the baby is not statistically nor medically foreseeable. Thus, the AED is used to potentially restart the heart and restore the patient’s regular heart rhythm. Lastly, if at any point the patient becomes responsive, the pregnant woman can be positioned on their left side. This position will allow for better blood flow to their heart and to the baby. Why is it important to provide cpr to a pregnant woman?Whether a pregnant woman or a non-pregnant individual, you should administer CPR immediately in the event that you are medically assisting an unconscious victim who is not able to breathe. When a patient is in cardiac arrest, their bodies are not delivering an adequate supply of blood to the brain and other organs. For any patient, this can lead to serious complications. In pregnant women, this could potentially impact the health of the fetus. When a patient is pregnant, they require 30-50% more blood flow in order to accommodate both the mother’s and the baby’s needs. Because of this, “pregnant women are particularly vulnerable to oxygen deprivation caused by cardiac arrest.” As such, in the event of cardiac arrest, CPR is critical so that blood flow is restored and the patient and fetus continue receiving oxygen. The AHA explains that pregnant women are experiencing cardiac arrest at an increasing rate, and around 1 in 12,000 admissions for delivery in the U.S. results in a maternal cardiac arrest. These increasing statistics involving cardiac arrest among pregnant women are thought to be caused by a number of conditions, including heart failure, amniotic fluid embolism, or hemorrhage. Get CPR certified WITH HELP-A-HEART CPRAre you ready to get CPR certified?
Our CPR and First Aid certification courses at Help-A-Heart CPR will cover everything you need to know to provide care while administering CPR to both pregnant and non-pregnant individuals. Our professionally trained and experienced instructors and engaging and hands-on learning environments provide an empowering and educational experience for every student. With a wide selection of class day and time options, it’s easy to fit training into your busy schedule. If you would like to get your entire workplace or team trained at once, we’re happy to provide a quote for group CPR training. Or, you can explore our online BLS course options for a hybrid certification with a short skills check with one of our instructors at our office. To get started, contact us by phone at (210) 380-5344 or online through our contact form. We can’t wait to hear from you! How To Operate An AED In 6 Steps!Timing is vital when a sudden cardiac arrest event occurs. The immediate use of an automated external defibrillator (AED) can increase survivability after cardiac arrest. So what are the 6 basic steps to operating an AED? Even though AEDs are designed to be extremely user-friendly, understanding how the specific AED operates and what the specific steps for using the AED can increase your confidence and provide you with the added skills to actively save a life. What is an AED?The AED is a device used to treat victims of cardiac arrest and it most often used in conjunction with CPR. The AED conducts an analysis of a patient’s heart rhythm to determine whether a shock is needed to restore a normal heartbeat and if it determines that a shock is necessary, it delivers a shock to the patient using an electrical current called joules. Unfortunately, there is a common misconception that AEDs are dangerous and could cause harm to the operator or other bystanders. In reality, AEDs are a safe, effective tool that pose little risk when used properly. Why Are AED's Important? An AED is a life-saving device that can significantly increase a patient’s survivability after cardiac arrest. According to the National Institute of Health (NIH) (2022) cardiac arrest victims had a 67% chance of survival when a bystander uses an AED, as opposed to just 43% when they wait for emergency medical responders to arrive. Subsequently, AEDs are an highly effective way to provide emergency care to individuals quickly while waiting for emergency response personnel. How Do you operate an AED?Operating an AED is extremely easy! By following just a few steps, you can administer an electric shock in minutes and help restore the patient’s regular heartbeat. Did you also know that most AEDs include instructions? Many units are even equipped with voice prompts to walk the user through the process. However, despite the voice prompts, it is still imperative to know and understand the basic steps for AED use. the 6 Basic Steps For Operating An AED ARE:1. Assess the scene for safety! First, check the scene and make sure that it is safe to approach the victim. If there is another individual or bystander, have them call 911 for help and grab a first aid kit and AED if not already there. 2. Turn on the AED and follow the prompts! Once an AED is available, turn it on and begin following the prompts. Some devices will call out voice prompts while others show the steps on a screen. Also, listen to see if pad connectors need to be plugged in. 3. Attach electrode pads. Remove any clothing that is covering the victim’s chest. Attach one electrode pad to the upper right side of the patient’s chest, then place the other on the lower left side of the patient’s chest. 4. Check for shockable or non-shockable rhythm. Let the AED check for a shockable rhythm. Make sure that no one is touching the patient and call out “clear" or "stand back"! 5. Administer shock if necessary. If the AED determines a shock is necessary, make sure that no one is touching the patient and call out “clear” or "stand back"! Once it is safe to do so, administer the shock. 6. Administer chest compression CPR. Begin administering CPR with chest compressions. wOULD YOU LIKE TO Learn More?Now that you’ve learned a bit more about AED's, would you like to take one of our CPR/AED classes here at Help-A-Heart CPR? It doesn't matter if you are a future healthcare provider or a stay-at-home mom, getting CPR and AED certified is empowering.
If you have any questions, don’t hesitate to reach out! Our team of training professionals is passionate about CPR and we’re here to help in any way we can. Give us a call at (210) 380-5344 or use our online contact form. |
AuthorDr. Tracy A. Jones is the CEO of Help-A-Heart CPR, LLC and an American Heart Association, ASHI, and American Red Cross Master Program Trainer, Instructor, & AHA Faculty Member located in San Antonio, Texas. Archives
June 2024
Categories |
Help-A-Heart CPR, LLC | 1747 Citadell Plaza Suite 101 | San Antonio, Texas 78209 | (210) 380-5344 | [email protected]
Copyright © Help-A-Heart CPR, LLC 2024
100% Certification Acceptance
We promise your employer, school, or agency will accept the certification card we issue to you. If there is a question of acceptance or validity, simply send us an email at [email protected] with full details. We will reach out to the individual/entity and provide accreditation information. If still there’s a question, we will provide you with a full refund of your class fee. It’s that simple.
We promise your employer, school, or agency will accept the certification card we issue to you. If there is a question of acceptance or validity, simply send us an email at [email protected] with full details. We will reach out to the individual/entity and provide accreditation information. If still there’s a question, we will provide you with a full refund of your class fee. It’s that simple.
|
Communities Served
ALABAMA: Birmingham
ARKANSAS: Fayetteville, Hot Springs, Jonesboro, Little Rock NEW MEXICO: Albuquerque TENNESSEE: Knoxville TEXAS: Amarillo, Arlington, Austin, Bandera, Bastrop, Boerne, Brownsville, Comfort, Converse, Corpus Christi, Dallas/Ft. Worth, Del Rio, Dripping Springs, El Paso, Floresville, Fredericksburg, Georgetown, Harlingen, Houston, Junction, Katy, Kerrville, Kingsville, Kingwood, Laredo, Lubbock, Lufkin, McAllen, Midland, New Braunfels, Odessa, Pleasanton, Round Rock, San Angelo, San Marcos, Schertz, Seguin, Taylor, Temple, Texarkana, Tyler, Universal City, Victoria, Waco, The Woodlands |
Why Choose Help-A-Heart CPR?
1. Flexible Scheduling
2. On and Off Location Training Available 3. Casual, Fun Atmosphere 4. Best Price Guarantee 5. All Instructors are AHA and/or ARC certified 6. 5 Star Google Reviews 7. Blended Learning (Online & Skills Check) Available 8. Meets OSHA & College CPR Requirements 9. Get Certified Within 3-4 Hours 10.Certification Is Good For Two Years 11. Official AHA/ARC/ASHI Training Site 12. High Quality Safety Training! |